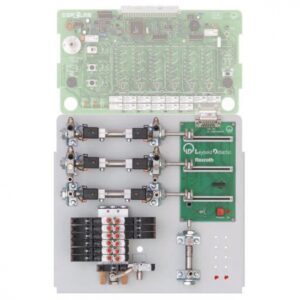
Opis
The experiments are carried out using machines of industrial manufacture. All the test machines are equipped with a special base for attachment to the Machine test system 0.3. The system allows the characteristics of the machines under test to be recorded. Power for the machines under test is provided either directly from the mains or via special laboratory power supplies.
Objectives
- Protective measures and electrical safety
- Setting up electrical machines and putting them into operation
- Use of starting circuits
- Assessment of electrical machine characteristics
Features
- In order to protect against overheating, the stator windings of the test machines are equipped with temperature sensors
- Should overheating occur, the machine testing system automatically shuts down the machine under test, thus preventing any damage to it.
- The test machines are equipped with an educationally designed terminal board with the winding configuration printed on it.
- The ends of all the windings are connected to the terminal board and can be accessed via 4-mm safety sockets.
- Computer-supported acquisition of measurement data provides for meaningful measurement results.
The actual area of application for synchronous machines is as generators. They are used in many forms, from a small shaft generator to supply energy for a ship (output in the kW range) right up to hydrogen-cooled power station generators (output in megawatts). Topics investigated include run-up, excitation and efficiency as well as the various types of loading. One interesting aspect in the subject of power station control, which is handled in greater detail as part of the topic Electric power supply technology.
The complete equipment set is equally suitable for student experiments in laboratories with low voltage supplies (400 V three-phase) and for setting up on a mobile trolley for demonstration by teachers in a classroom. The procedures for the experiments are provided in a printed manual.
The target group is made up of commercial apprentices and students of electrical machine construction. The course offers experiments at an intermediate level and also allows for the necessary insight into machine behaviour for scientific interpretation at undergraduate level.
Synchronous motor topics
- Non-salient-pole and salient-pole rotors
- Voltage equations
- Equivalent circuit and vector diagram
- Operation with no-load and with a permanent three-pole short-circuit
- Locus diagrams and control characteristics
- Torque and loading
- Potier diagram and armature reaction
- Synchronisation and use of multiple machines in parallel
- Starting methods for synchronous motors
- Control of reactive power
- Power performance
Synchronous generator topics
- Voltage generation
- Excitation of synchronous machines
- Operating response
- Armature current and torque
- Braking operation and locus diagrams
- Starting and synchronisation
- Single-phase generators
Similar to illustration